Shoulder Replacement
Shoulder replacement is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased shoulder joint is replaced with an artificial implant. It is commonly performed to relieve pain and restore mobility in patients with severe arthritis, rotator cuff injuries, or fractures.
Types of Shoulder Replacement:
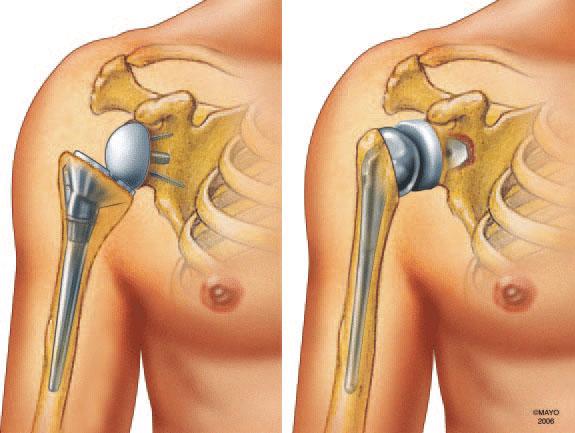
- Total Shoulder Replacement (TSR): Both the ball (humeral head) and socket (glenoid) of the joint are replaced with artificial components.
- Partial Shoulder Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty): Only the humeral head is replaced, while the natural socket is preserved.
- Reverse Shoulder Replacement: The positions of the ball and socket are reversed, often used for severe rotator cuff damage or complex fractures.
Procedure:
- The damaged humeral head is removed and replaced with a metal or ceramic prosthetic ball.
- The socket may also be resurfaced or replaced with a plastic component.
- The new joint components are secured with bone cement or a press-fit technique that allows natural bone growth.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- Hospital stay of 1–3 days.
- Physical therapy is essential for regaining shoulder strength and range of motion.
- Full recovery can take several months, depending on the type of replacement and individual healing.
Benefits:
- Significant pain relief
- Improved shoulder function and mobility
- Enhanced quality of life
Risks:
- Infection
- Implant loosening over time
- Nerve damage
- Stiffness or limited range of motion
Shoulder replacement is a highly effective procedure that can help patients regain movement and reduce pain.