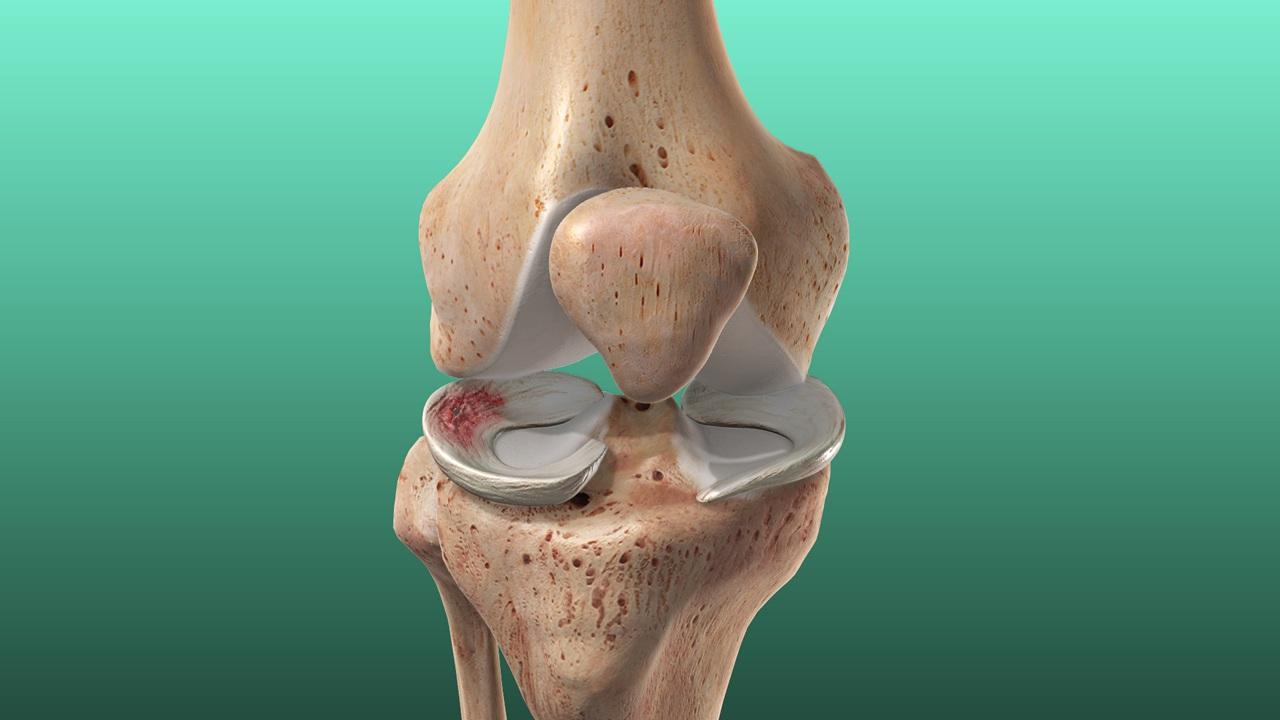
Meniscal Tear Injury
A meniscal tear is a common knee injury affecting the meniscus, which is a C-shaped cartilage in the knee joint that provides cushioning and stability. Meniscal tears can occur due to trauma (acute injuries) or degeneration (wear and tear over time).
Types of Meniscal Tears
- Radial Tear – Most common, occurs in the middle of the meniscus.
- Horizontal Tear – Splits the meniscus into upper and lower layers.
- Vertical (Longitudinal) Tear – Runs along the length of the meniscus.
- Bucket Handle Tear – A severe type of longitudinal tear where a piece flips over.
- Flap Tear – A portion of the meniscus is displaced, causing catching or locking.
- Degenerative Tear – Due to aging and wear, common in older adults.
Causes of Meniscal Tears
- Sports injuries (pivoting, sudden stops, or deep squatting).
- Trauma (direct hit or twisting force).
- Aging and degeneration (weakened cartilage over time).
- Knee instability (previous ligament injuries like ACL tears increase risk).
Symptoms
- Pain (especially when twisting or rotating the knee).
- Swelling (within hours or days after the injury).
- Locking or catching sensation.
- Clicking or popping sounds in the knee.
- Instability or difficulty fully straightening the knee.
Diagnosis
- Physical Exam:
- McMurray Test – Pain or clicking with knee rotation.
- Apley’s Compression Test – Pain when pressing down on the knee.
- Imaging:
- MRI – Best for detecting meniscal tears.
- X-ray – Rules out fractures or arthritis.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical (Conservative) Treatment
- RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation).
- NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen) for pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy to strengthen the muscles and restore mobility.
- Bracing for support.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is needed for:
- Large tears, displaced fragments, or locked knees.
- Tears that don’t heal with conservative treatment.
Types of Surgery
- Arthroscopic Meniscectomy – Removal of the damaged part of the meniscus.
- Meniscus Repair – Stitching the torn meniscus together (best for younger patients and peripheral tears).
- Meniscus Transplant – Rare, for severe damage with cartilage loss.
Recovery & Rehabilitation
- Non-Surgical: 4-6 weeks with PT.
- Meniscectomy: 4-6 weeks recovery.
- Meniscus Repair: 3-6 months (longer healing due to suturing).
- Rehab includes strength training, flexibility exercises, and gradual return to activity.